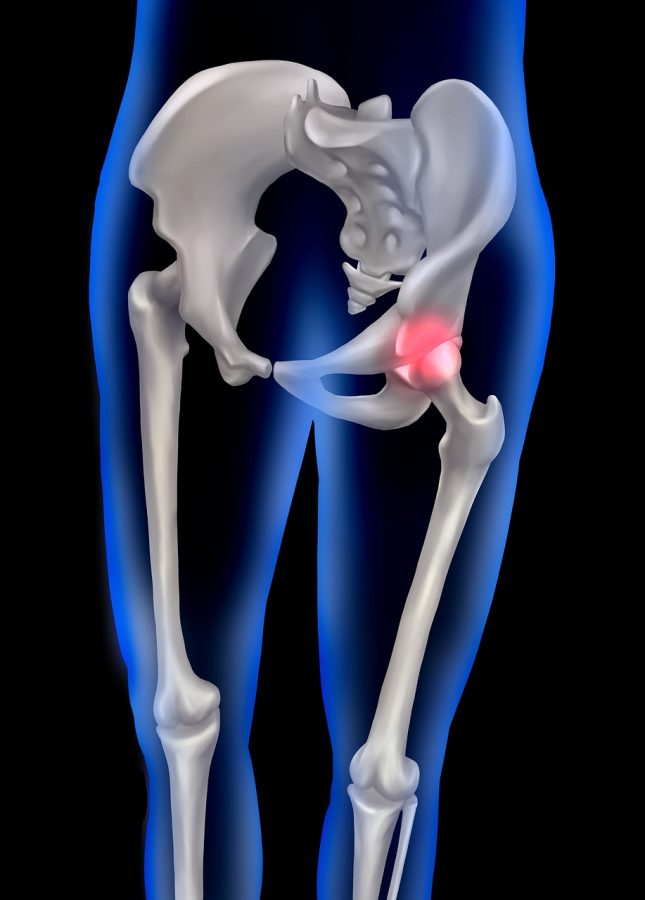
Hip joint pain at 40 is one of those problems people rarely expect but often recognize instantly. At first, it feels minor — a bit of stiffness after sitting too long, an odd discomfort when getting out of a car, a dull ache after walking more than usual. Many ignore it. Others assume it’s temporary. But for a surprising number of adults, hip joint pain at 40 becomes a quiet background issue that slowly shapes how they move, sit, and even sleep.
What makes this kind of pain frustrating is not just the discomfort itself, but the uncertainty around it. Is this normal aging? Is it muscle-related? Or is something deeper happening inside the joint? Hip joint pain at 40 often sits right in that grey zone where symptoms are real, but explanations feel blurry.
Quick Action Plan
- Interrupt long sitting every 30–45 minutes with short movement breaks.
- Build basic strength in glutes and core muscles two times per week.
- If pain lasts more than 2–3 weeks or limits daily life, get medical advice.
Sources: Harvard Health, Mayo Clinic, NIH / NIAMS
One reason hip joint pain at 40 feels so confusing is that it rarely comes from a single dramatic cause. There is usually no clear injury, no moment you can point to and say, “That’s when it started.” Instead, the pain builds quietly, shaped by years of habits that once felt harmless.
Why hip joint pain becomes common around 40
By the time people reach their 40s, their bodies carry the history of how they’ve lived. Long periods of sitting, limited movement variety, weak stabilizing muscles, and gradual weight gain all leave traces. Hip joint pain at 40 is often the point where these traces finally speak up.
The hip is designed to be strong and adaptable, but it depends heavily on surrounding muscles to distribute load properly. When glutes become weak and hip flexors stay chronically tight, the joint itself starts absorbing stress it was never meant to handle alone. That stress doesn’t announce itself loudly. It shows up as stiffness after rest, discomfort when standing up, or a deep ache after walking or climbing stairs.
Many people with hip joint pain at 40 notice that the pain isn’t constant. It comes and goes. One day feels fine, the next feels wrong. This inconsistency is exactly what makes people delay action.
The role of sedentary life
Sitting itself is not the enemy. The problem is how much of it fills modern life. Hours spent in chairs shorten hip flexors, reduce circulation, and teach glutes to switch off. Over years, the body adapts to this position — and those adaptations are not kind to the hips.
When support muscles don’t engage properly, hip joint pain at 40 becomes more likely. The joint begins to carry loads unevenly, especially during walking. Small changes in movement patterns then ripple outward, affecting knees and the lower back. This is why hip discomfort so often comes bundled with other joint complaints.
What makes sedentary-related pain tricky is that exercise alone doesn’t always fix it. You can train hard a few times per week and still sit badly for ten hours a day. The hip responds to what you do most, not what you do occasionally.
Body weight and joint load
Weight plays a straightforward role in hip joint pain at 40. Every extra kilogram increases the load passing through the hips with each step. This doesn’t mean pain is inevitable if you carry extra weight, but it does mean the margin for error shrinks.
Even modest weight reduction can noticeably reduce discomfort. Less load means less compression inside the joint and less strain on surrounding tissues. For many people, this change alone shifts pain from “daily background issue” to “occasional warning sign.”
Common causes behind hip joint pain at 40
In most cases, hip joint pain at 40 develops from a combination of factors rather than a single diagnosis. Muscle imbalance is extremely common. Old injuries that never fully healed play a role. Excess body weight adds constant stress. And for some, early degenerative changes begin quietly.
Arthritis at this age often doesn’t look dramatic. It shows itself as stiffness after rest, reduced tolerance for long walks, or a deep, dull ache rather than sharp pain. Because symptoms are subtle, many people dismiss them until patterns become harder to ignore.
Symptoms that deserve attention
Not all discomfort is equal. Mild stiffness that eases with movement is common. But hip joint pain at 40 should not be brushed off when it becomes sharp, persistent, or disruptive.
Pain at night, catching or locking sensations, visible swelling, or increasing difficulty with normal walking are signs that something more than simple muscle tension may be happening. These are moments where waiting it out rarely helps.
Movement and exercise
The goal of exercise is not punishment. It’s support. Low-impact activities like walking, cycling, and swimming help nourish the joint without overwhelming it. Strength training focused on glutes and core restores balance that protects the hip.
For many, hip joint pain at 40 improves not from doing more, but from doing things more consistently. Short, regular movement beats sporadic intensity.
When to see a doctor
If pain lasts longer than two weeks, limits daily life, or steadily worsens, medical evaluation is the sensible next step. Early assessment can rule out conditions that benefit from early treatment and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
Posture and daily habits
Posture might sound boring, but it quietly shapes joint load all day long. Chair height, foot placement, how you stand up, and how often you move all influence hip stress.
For many people with hip joint pain at 40, small adjustments done consistently bring more relief than dramatic interventions done briefly.
Final thoughts
Hip joint pain at 40 is not a verdict. It’s feedback. For some, it’s a warning sign that habits need adjustment. For others, it’s an early signal to get informed and act before limitations grow. The earlier you listen, the more options you keep.